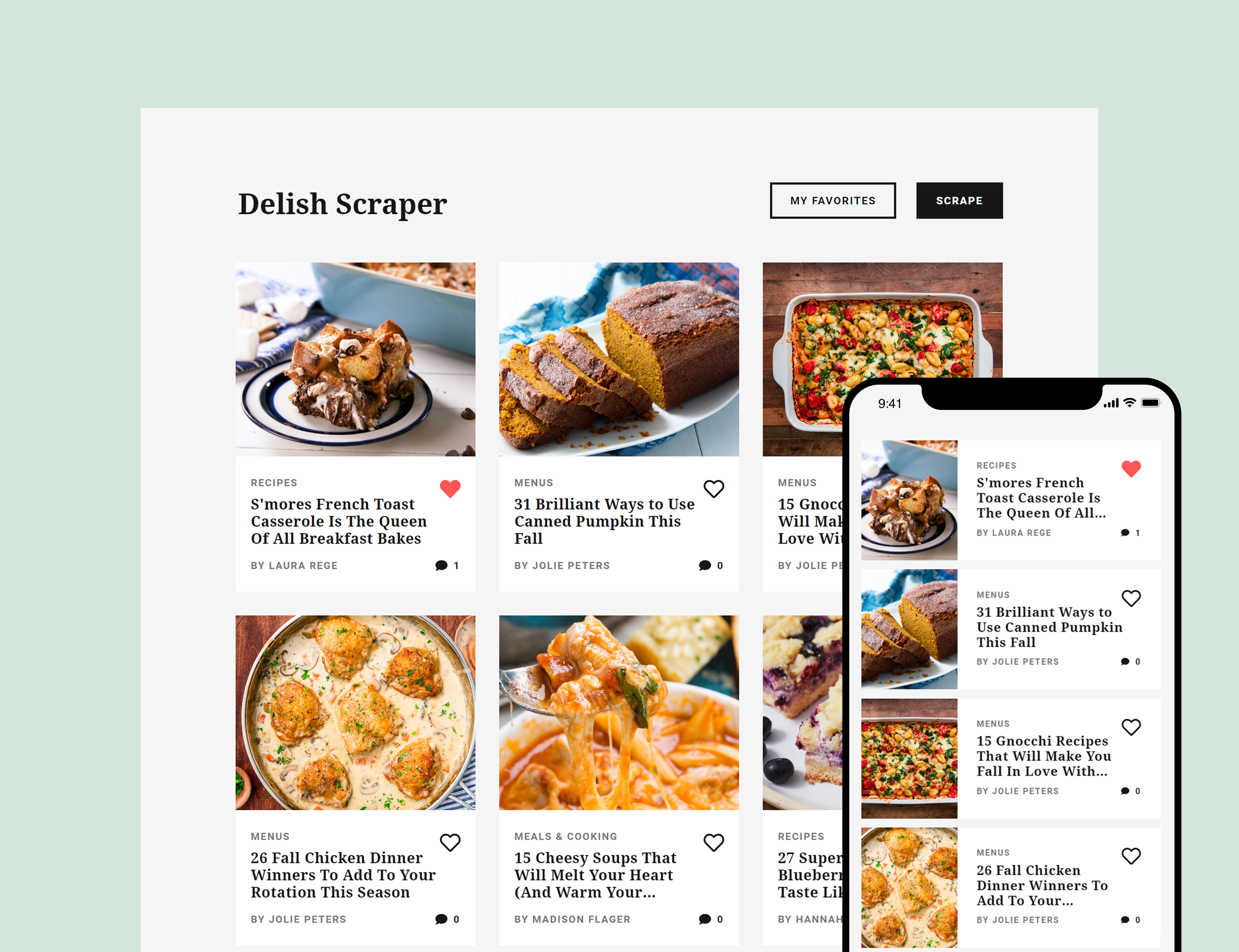
Delish Scraper
Delish Scraper is a food news and recipe scraping application that pulls and displays articles from Delish for users to save (or unsave) and add comments either under a name or anonymously. All data from the scraped articles and individual comments are stored in the MongoDB database.
User Stories
One of UT Austin Coding Bootcamp’s full-stack assignments is to build a news scraper with the following user stories:
- I can click a button and have new articles from a news outlet populate the page.
- I can favorite and unfavorite an article and see the update occur real-time.
- I can add comments to any article and see other comments.
Development Process
- A
GETrequest gets sent when the user clicks on the Scrape button to pull article information from Delish using Axios. Axios then returns a response that contains the HTML markup of the webpage. The response data is loaded into Cheerio, a implemention of jQuery within the server side. - Targeted data from each article entry is inserted into the
Articletable inside MongoDB using acreate()method. To prevent the same articles from being created in the database, each title property is set as unique within the Mongoose schema. Comments are also associated with each article using thepopulate()method. - Clicking on the heart icon sends a
PUTrequest to change the saved state of the article using anupdate()method. If an article is favorited, the saved state is set to true and vice versa. - The comment property in the
Articlemodel is set to an array. When a user submits a comment, a new instance is inserted in theCommenttable usingcreate(). Afterwards, it is then pushed into the comment property of the specific article using afindOneAndUpdate()method, where the article is found by id and updated with$push. - Express-Handlebars, an Express view engine, reloads the page
upon every change in the database to display all updated information with the assistance of built-in helpers. Helpers such as
{{#if}}and{{#unless}}works as boolean conditionals and renders data accordingly. Some examples are changing the display when toggling between saved states and showing the number of comments per article.